
Image Courtesy: Intel
TMT Predictions 2021
Technologies for measuring athletes’ health and performance are transforming how they train, compete, and manage their careers. But this explosion of athlete data is raising new questions about how best to use it—and how to do so ethically.
From cricket to hockey, baseball to basketball, the digital transformation of sports is in full swing. Clubs, teams, leagues, broadcasters, venue operators, and athletes increasingly see the value in analytics and are working to realize that value. Technologies such as computer vision, machine learning, advanced wireless connectivity, and wearable sensors are transforming how athletes train, compete and manage their careers. This explosion of data, however, is raising new questions about how best to use it—and how to do so ethically. To begin to address such concerns, we predict that by the end of 2021, multiple professional sports leagues will establish new formal policies around the collection, use, and commercialization of player data.
Data is fundamentally changing sports
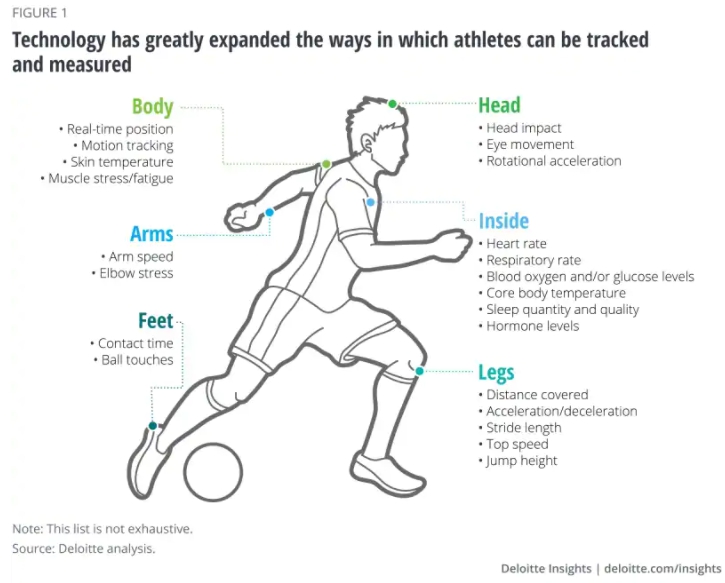
If measuring something in sports is conceivable, chances are that someone somewhere is already measuring it. Hundreds of different metrics can be analyzed today through video analytics and wearables such as harnesses, sleeves, bands, straps, rings, and smart fabrics. Over the past decade, the use of analytics in sports has slowly transformed everything from how talent is identified and assessed to how athletes are trained and managed to how games are played on the field, court, and pitch. The data and analytics revolution has begun to blur the boundaries between many disparate areas of sports, including esports, virtual sports, gaming, broadcasting, fantasy sports, betting, and the live-venue experience. As the use of data and analytics in sports matures, the industry will likely have to address issues about not just the enabling technology, but also increasingly about data rights management, privacy, regulations, monetization, and new ways to experience sports.
Almost all of the world’s major professional sports teams have one or more analytics experts on staff with the mandate to find any advantage that can improve the team’s chances of winning. In basketball, video capture and analysis have yielded insights that have led to more three-point shots and a greater emphasis on player-load management. In baseball, intensive statistical analysis of what works and what doesn’t, has dramatically changed pitcher management, increased the use of the “shift,” and replaced the small ball with swinging for the fences. Similar analyses now inform how American football teams approach fourth downs and the way soccer teams select shots.
The difference today is that data collection and analysis are becoming increasingly real-time, and it is happening not just on the field and in the gym but around the clock. Further, it is now possible to measure indicators inside as well as outside the body; new layers of positional, biometric, and biomechanical data are creating hundreds of new metrics to feed into decision-making. Finally, advancements in computing power, cloud technology, machine learning algorithms, and high-speed video capabilities are enabling ever more powerful ways to collect and crunch numbers. In this era of the hyperquantified athlete, the increasingly urgent question is how to get from data collection (which is easy) to actionable insight (which is hard) to potential monetization (which is really hard)—all the while protecting athletes’ rights, ensuring fair play and competitiveness, and meeting the financial needs of leagues, players, and owners.
The state of play
For purposes of this article, we will focus on two main types of data that are typically collected from athletes:
• Positional/tracking data. Positional/tracking indicators measure, in three dimensions, exactly where a player—or ball, puck, or other object—is located on a field or court. This data can include metrics such as position, acceleration, lateral motion, speed, jump height, and other measures. The data is collected either through video analytics or by sensors in combination with global satellite positioning systems and ground-based wireless networks.
• Biometric data. Biometric data refers to any kind of biological information from an individual player. These metrics could include everything from pulse rate and blood glucose or oxygen levels to sweat rate and sleep rhythms. Some biometric measurements, such as heart rate, have been used for decades; now, through digital sensors and ubiquitous low-latency communication networks, many more measurements can be made, in more physical locations, at a greater speed.
The market for quantifying athletes is both diverse and fragmented, with a broad range of options for sensor technology, computing power, data storage, and advanced analytics. Purveyors of these technologies range from “sport tech” companies such as Catapult, KINEXON, Stats Perform, and Zebra to tech giants such as Amazon Web Services, IBM, and SAP, as well as a plethora of startups. The broader sports tech market has also seen a great deal of venture capital interest in recent years, with over 3,000 global deals and funding rounds between 2014 and late 2019.
Most, if not all, of the world’s major sports leagues, are using these technologies and techniques in various ways. In doing so, they are expanding their view beyond just the technology to how they balance the technology’s use with players’ and coaches’ needs. For example:
• Beginning in 2014, the NFL began using radiofrequency identification (RFID) tags in players’ shoulder pads, balls, and various areas of the field. Each team is provided their own raw data from that system to analyze and use as they see fit.
• The National Hockey League (NHL) has been experimenting with puck and player tracking for years. After demonstrating the latest iteration of these technologies at its 2020 all-star game, the league is beginning to incorporate them fully.
• Players in the Australian Football League have been using positional sensors and heart rate monitors during games for the last few years. They even use the data to make in-game adjustments.
• In 2017, Major League Baseball (MLB) approved the use of Whoop straps by players on a voluntary basis to track information that they can use later to better understand their performance. This is in addition to other approved wearables that allow players to measure factors such as arm stress.
A competitive edge through hyperquantification
The famous cycling coach Sir Dave Brailsford once said, “It struck me that we should think small, not big, and adopt a philosophy of continuous improvement through the aggregation of marginal gains.” Hyperquantification is helping teams, leagues, and players discover these gains across the life cycle of their sport—talent identification, training, pregame preparation, gameplay, postgame analysis, and rest and recovery. Of these, three areas that could see further innovation in the near future are:
Talent identification. If a team is going to make a significant financial investment in a player, it wants to be confident that the player has the skills, raw physical ability, medical profile, and mental makeup to succeed. This process is becoming more virtual, especially in the wake of COVID-19. In addition to traditional in-person assessments, teams are increasingly using automated video analysis and positional and tracking data in their scouting. These advances have helped to expand the pool of potential professional players to include those that scouts may not be able to travel to see. For example, one pro football hopeful could not attend traditional scouting events due to personal injury and the COVID-19 pandemic, so he submitted his player-tracking data from college games to prove his speed in a real-world environment. In the near future, more biometric data will likely be added to the mix to augment medical data for predicting long-term performance. One day, teams could have access to a player’s biometric data from his or her participation in youth sports through high school and college programs. While data is unlikely to completely replace traditional evaluative methods, it is poised to provide another set of objective measures that will likely become more and more important.
In-game decision-making. Today, most biometric data collection and analysis happen during training and practice, or to help with post-game evaluations. Its use is still not widespread in actual games, and even if in-game data is collected, it typically is not used for any immediate coaching decisions. In fact, some leagues prohibit the in-game collection and use of biometrics unless explicitly approved by the league. On the other hand, in-game positional and tracking data is already widely used. Leagues such as the NFL, NHL, and the Mexican football league Liga MX have all done this to some extent, and they have gained better insight into how game strategies are working. As teams gain more experience and data collection becomes easier and analysis faster, real-time analytics that guide how coaches and managers direct their teams may come into wider play, identifying who might be at risk of injury, who is getting close to exhaustion, who might be out of position, and who may be primed to make a big play.
Injury reduction. The holy grail for many athletes and teams is being able to predict when conditions may heighten the risk of injury. For teams, it means more wins and more revenue; for athletes, it means having information that can help them extend their careers—and earnings potential—as much as possible. Predicting injuries more effectively requires measures that help balance exertion and strain with the proper amount of recovery time and sleep. The potential benefits are vast: One study estimated that the NFL lost more than US$500 million in 2019 due to injuries. It’s no wonder that the NFL recently partnered with Amazon Web Services to use machine learning and computer vision technologies, powered by multiple different data sets, to gain insight into head and other injuries.
From measuring to monetizing
The hyperquantification of athletes can provide more efficient training, improve competitiveness, and increase the likelihood that star athletes stay healthy—benefits that, as organizations well know, can potentially lead to higher attendance, more sponsorships, and greater broadcast viewership.
What may be significantly harder is to figure out how this digital revolution can create new revenue streams for teams, leagues, and players themselves. Although innovations are taking place in smaller sports, many major leagues are just starting to test how they can monetize players’ biometric and positional data, with some leagues even banning the commercialization of player data. There is still much to be done to establish clear data-ownership policies, provide equitable revenue distribution, and ensure player protections. But the potential for monetizing player performance data is so great that it will likely encourage the involved parties to begin addressing these concerns in the short to medium term.
We see several areas for experimentation and innovation over the next few years:
Fan engagement. Leagues and players’ associations can work with broadcasters and venue operators to use player data to improve the fan experience and create new ways for fans to engage with sports and athletes. This could lead to new direct-revenue streams, generate new marketing and sponsorship opportunities, and/or have a halo effect on already established revenue streams. For example, the Professional Squash Association (PSA), working with Sports Data Labs, tracks and displays players’ heart rates in real-time during broadcasts. The goal is to give fans a better understanding of the game’s athleticism as well as create more excitement around the gameplay; any revenue generated through the biometric data is shared among the league, players, and partners. Similarly, the handball league LIQUI MOLY Handball-Bundesliga has teamed up with KINEXON and Content Stadium to stream real-time player performance information in stadiums and across social media platforms.
Licensing. Another way for players and leagues to make money is by licensing player data to organizations such as fantasy sports leagues, sportsbook companies, broadcasters, and health and fitness companies. In 2017, the NFL Players Association came to an agreement with Whoop that, among other things, allowed players to sell their personal health data collected by the wearable. Many leagues already have strategic partnerships with sportsbooks, such as the PGA Tour with DraftKings and the NBA with William Hill, laying the groundwork for emerging opportunities. Other types of opportunities also exist: During its short life, the Alliance of American Football, in partnership with MGM, was developing an application that would enable betting during games where odds would be adjusted based on data from player wearables.
One league that sees such opportunities clearly is the WNBA. In its recently enacted collective bargaining agreement with players, they recognized the potential for data collection and use, saying that “the use of wearables and other in-game technology provides a unique opportunity for the WNBA with respect to enhanced broadcasts, differentiated fan experiences, player health, and revenue generation.”
Key matchups
Any opportunity to improve athlete performance or to increase the amount of money in sports is clearly extremely appealing. However, no emerging technology or change in approach is without consequences, some expected, some not. We see three critical areas that should be addressed if hyperquantification is to come into its own:
Quantity vs. quality. Coaches and their staffs have traditionally relied on gut feel and experience. Even today, some use analytics more widely than others, striking their own balance between data and instinct. With new positional and biometric data added to the mix, the analytics becomes more complex and the insights harder to communicate. To heighten the data’s utility, much work should be done to determine what measures are most critical—what data will truly make a difference, and what will merely create noise in the system. There is also debate over whether to believe the data overseeing results with one’s own eyes. Are there ways to properly quantify the magic of once-in-a-generation players? Finally, some worry that overanalysis will lead to a less entertaining product for fans, essentially “ruining” sports. For example, in MLB, longer games and less action (more strikeouts and home runs) can be attributed to the extensive use of analytics.
Performance vs. privacy. Questions abound about who ultimately owns player data, including any sensitive health information that teams could collect. A number of professional sports leagues in the United States have established guidance and rules around this issue in their collective bargaining agreements with players’ associations. These rules specify how player data can be collected, whether or not its collection and use is voluntary, how it will be protected, and how it can be used. Some leagues have also established sensor and wearable committees that approve device and data use. For example, the NFL states that “each individual player owns his personal data collected by sensors,” while the NBA’s collective bargaining agreement says that “a player will have full access to all data collected on him from approved wearables.” But although these agreements do afford some protections and benefits, the speed of technology development and the rapid evolution of potential commercial opportunities are not necessarily compatible with the long-term nature of collective bargaining agreements, which last years.
A focal point in this debate is what is best for players. Many athletes are uneasy about using wearables to collect their data, especially biometric data. Some feel like they are part of a laboratory experiment, while others worry that, even though such use is prohibited, biometric data collection could bias contract negotiations. Some also voice concerns that required data collection will increasingly encroach on activities outside of work, such as sleeping. An example of this conflict is “Project Red Card”: A group of hundreds of former and current soccer players in the United Kingdom are suing sportsbooks and data-processing companies, claiming that they have illegally profited from player statistics. The details of this lawsuit are still emerging, but the results could eventually shape how many types of player data can be commercialized, as well as who ultimately profits.
Betting vs. banning. By some estimates, the global sports betting market is predicted to top US$150 billion by 2024. With the 2018 repeal of the Professional and Amateur Sports Protection Act in the United States, and the legalization of sports gambling by many US states, American leagues, in particular, are hungry to tap into new revenue sources. One of the emerging issues in this space is the potential for using individual athlete data for bets, either through using biometric and positional data to set odds, or by betting on specific measures such as pulse, top speed, and acceleration. Such uses could generate substantial pushback from players, who may see it as a gross invasion of privacy—but it could be a different story if they could significantly profit from it. The state of Illinois has gotten ahead of the curve by banning the use of biometrics in sports betting unless the relevant players’ association gives permission. Even though the desire for this type of wagering exists, the devil is in the details, and players, leagues, unions, legislators, and commercial businesses should all come to the table to decide what is best.
The bottom line
In the near future, it may become commonplace for fans sitting in a stadium or arena to look up at the scoreboard and see players’ top speeds in real-time, or a ranked list of players’ level of physical exertion during the game. The same information could also be broadcast to viewers at home and streamed on social media. Fans, both at home and in person, could use their mobile devices to place a bet in real or virtual currency on the outcome of the next play, with the odds influenced by positional and biometric data. Ideally, this would all be backstopped by robust agreements among all involved that guarantee voluntary collection of data, protect players’ rights, provide for proper data security and privacy, and set out detailed licensing and compensation rules.
These issues should be approached with great care, as the emerging hyperquantification landscape has the potential to become much more complex in the near future. As Yogi Berra once famously said, “If you don’t know where you are going, you might wind up someplace else.” Critical open questions include:
• How will advances in computer vision such as automated video analysis, sensor technologies, and machine learning accelerate the state of the art?
• Would players benefit enough financially from sharing their personal and performance data to entice them to do so?
• Will a standard agreement emerge between players and leagues across sports around the collection, use, and monetization of private and sensitive information?
• How will performance data ultimately be used to enhance the in-stadium and remote fan experience?
For the hyperquantification of sports to succeed, the athlete should be at the center of every decision and conversation. Athletes, trainers, coaches, player agents and representatives, and business leaders should become knowledgeable about the enabling technologies and their responsible use. Those collecting and using the data should convincingly demonstrate and effectively communicate its value. Athletes should see that it is in their best interest to share their data and allow for its thoughtful application. Above all, it is critical that trust be built and maintained among all parties. Without it, the potential gains may never be fully realized.
Authored By:
David Jarvis, Dan Jones, Kevin Westcott
Originally published in the Deloitte Insights blog.